I. Overview
1.1 Main uses and scope of application
ENSM fully automatic torsion spring testing machine is made in accordance with the technical requirements specified in the national standard JB / T7796-2005. This instrument is mainly used to test the torque-angle and angle-torque of various springs. It is a high-performance testing machine that can exert high-efficiency and labor-saving spring detection functions. place.
1.2 Product Features
1.2.1 1,2,3,4,5 sections of load (angle) spring constant number automatic test, free angle measurement can be easily completed.
1.2.2 The automatic origin correction function completes the calculation and compensation of the deformation of the load cell and the rigid structure of the machine material to ensure high-precision measurement.
1.2.3 Touch screen man-machine interactive test condition setting input is more convenient and quick.
1.2.4 To facilitate the calculation and input of tolerances, the system will automatically calculate the upper and lower limits after entering the tolerance percentage value.
1.2.5 There are more than a dozen test types, which can not only meet the production measurement, but also meet the testing requirements of spring engineering design.
1.2.6 The test load units are N.m, Kg.cm, and Lb.in.
1.2.7 For the convenience of operation, the measurement range can be freely converted into 5 test ranges.
1.2.8 Through the dial, the positions of the load test plug gauge and the rotary plug gauge are automatically corrected to obtain the accurate zero position.
1.2.9 The system is equipped with overload protection and emergency shutdown functions.
1.2.10 The system can set the number of repeated cycles for automatic testing by simple operation.
1.2.11 With data printing function.
1.2.12 Rotary displacement control button, with 10-degree, 1-degree, and 0.1-degree jog rotation levels, which can precisely control the angle.
1.3 Specifications
|
model |
ENSM-1 |
ENSM-3 |
ENSM-5 |
ENSM-10 |
ENSM-20 |
|
Torque (N.m) |
1 |
3 |
5 |
10 |
20 |
|
Minimum torque display value |
0.0001 |
0.0001 |
0.0001 |
0.0001 |
0.001 |
|
unit |
N.m, Kg.cm, Lb.in |
||||
|
Test speed |
1-1800deg / min |
||||
|
Manual rotation angle selection |
|||||
|
Test product diameter |
|||||
|
Test angle |
7200deg |
||||
|
turn around |
|||||
|
power supply |
AC 220V (110AC) |
||||
|
Overall dimensions (mm) |
697 * 450 * 623 |
||||
|
Weight (Kg) |
120 |
||||
Overall product structure
2.1 Outline structure
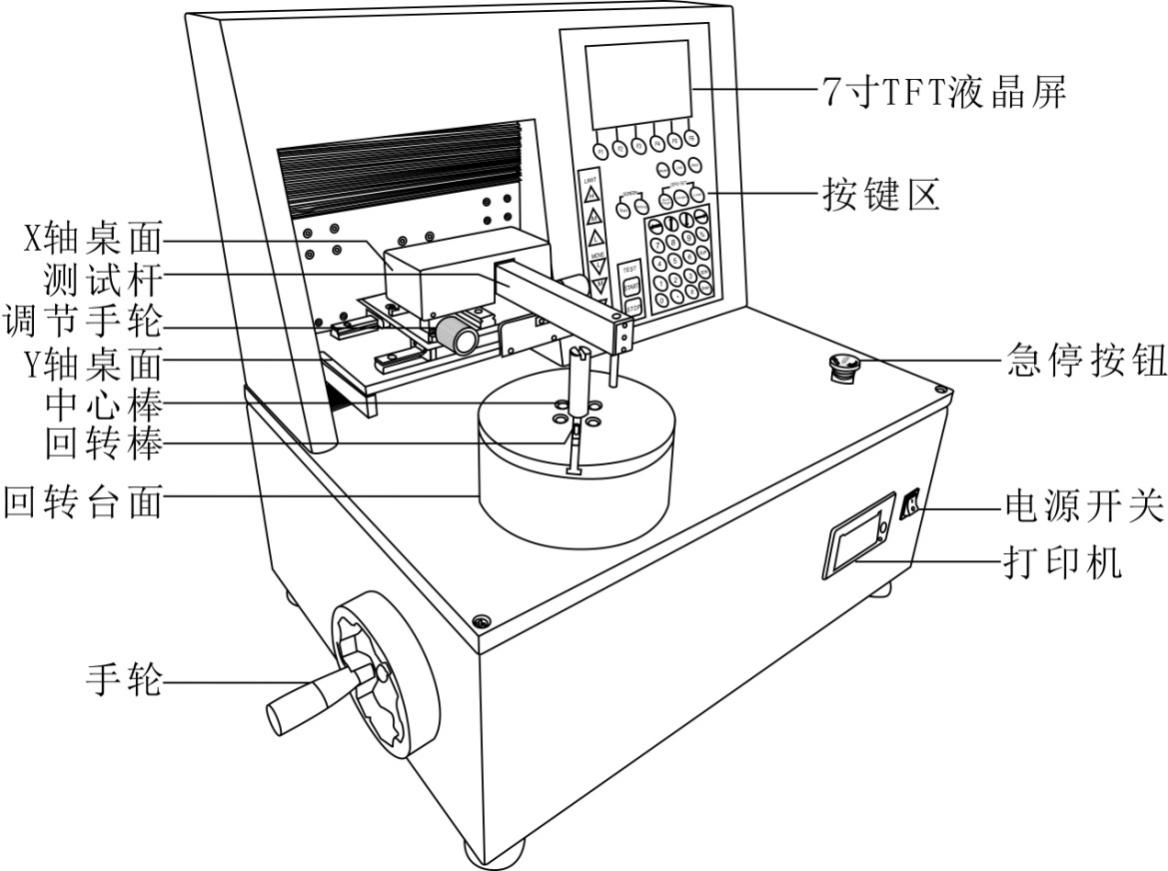
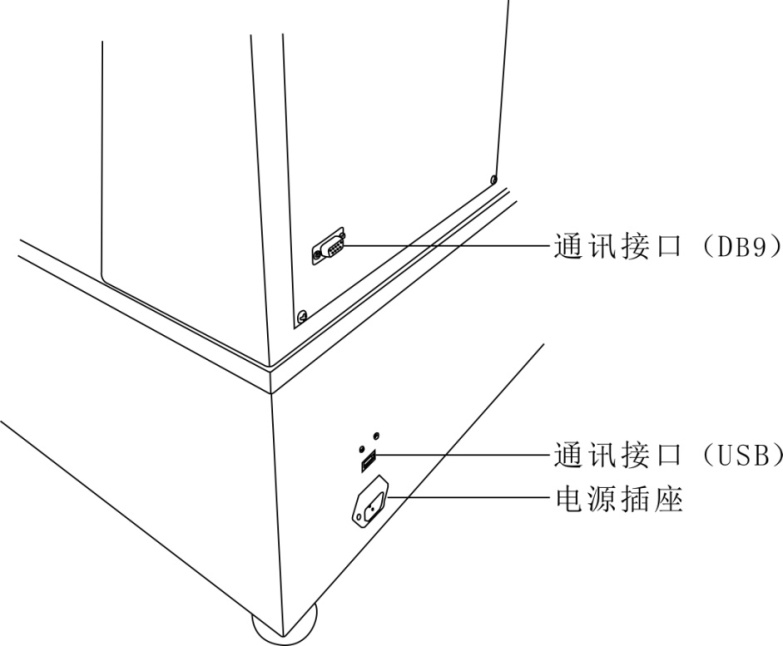
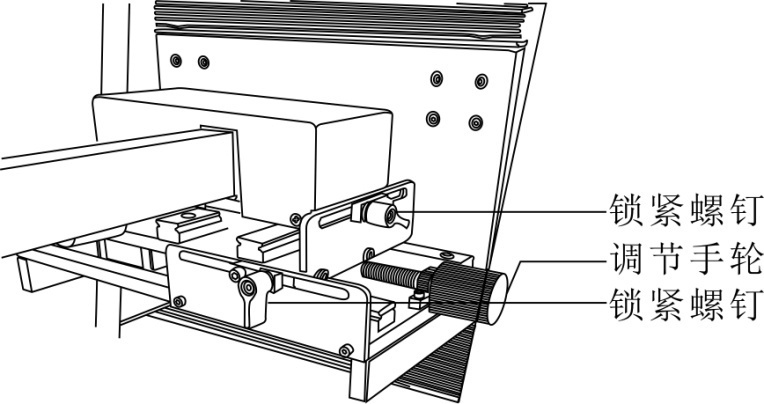
2.2 Key functions
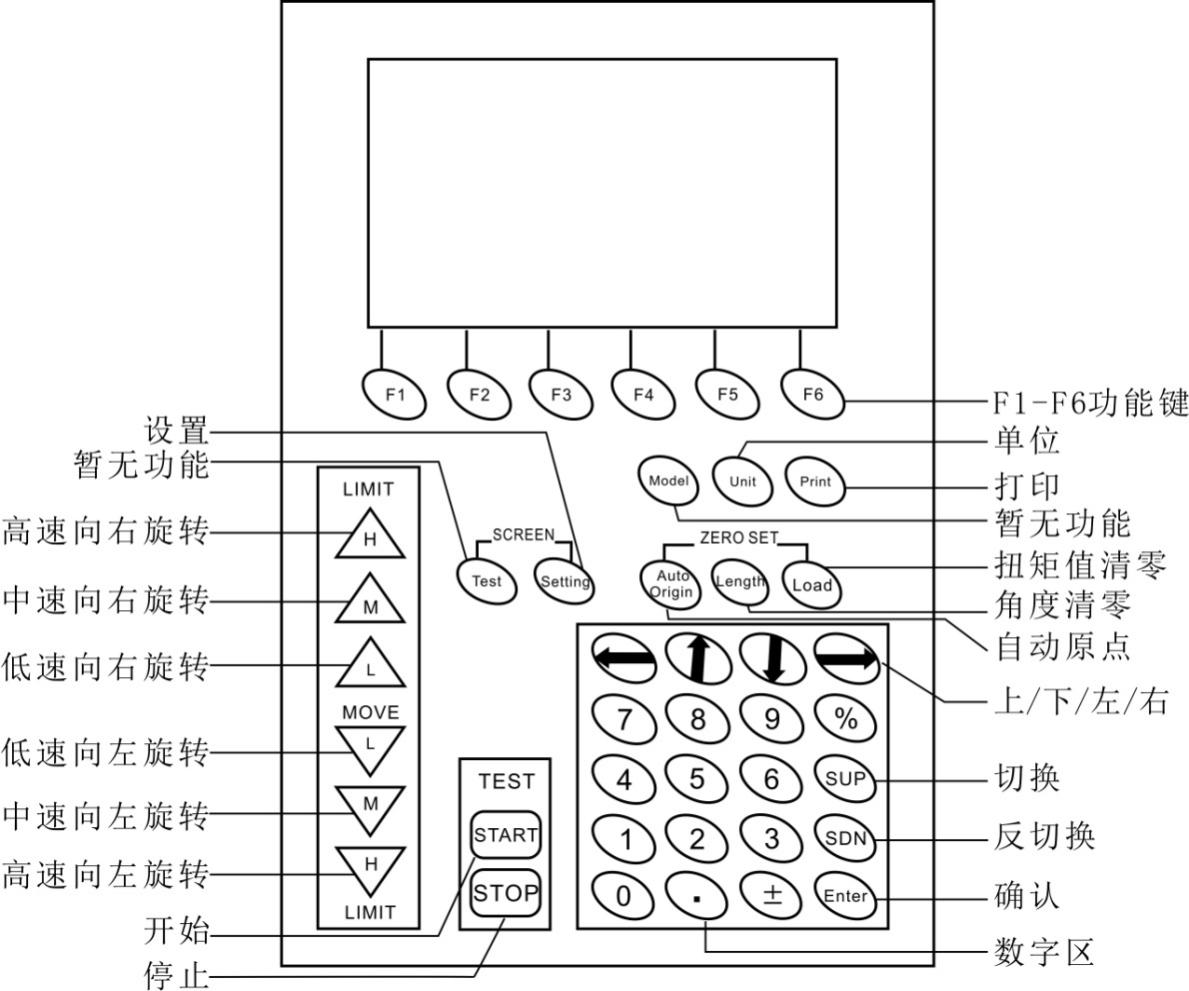
2.2.1 Function keys: The six function keys F1 ~ F6 are common to all interfaces of the instrument and correspond to the keys at the bottom of the screen after power-on.
2.2.2 High speed / medium speed / low speed rotate right, high speed / medium speed / low speed rotate left: These 6 keys have two functions: short press and long press.
Short press is used for single-step angle adjustment of rotary table, users can manually adjust the angle of rotary table according to their own requirements. For example, short press high speed to the right refers to the turntable facing right and runs at a high speed of 10deg, medium speed right refers to the turntable facing right to run at a medium speed of 1deg, and low speed to the right refers to the turntable facing right and runs at a low speed of 0.1deg.
If you press and hold these buttons for about 4 seconds, the rotary table can be moved up or down at a certain speed until the stop button is pressed or the protection mechanism is activated. The high, medium and low speeds correspond to 100deg / min, 50deg / min and 10deg / min respectively.
2.2.3 Unit key: Unit switching.
2.2.4 Print key: effective in real-time measurement interface and data storage display interface, short press print key in real-time measurement interface to print the currently displayed segment data; there are two printing methods in the data storage display interface, one is to print the current A small set of data can also be printed as a set of all repeated measurements.
2.2.5 Setting key: Press this key shortly to enter the system setting interface.
2.2.6 Automatic origin: short press this key, the spring will return to the free state and record the free angle.
2.2.7 Angle Clear: Press this key shortly to clear the angle display.
2.2.8 Clearing the torque value: Press this key momentarily to clear the torque value. Clearing the torque value must be effective when the motor is stopped.
2.2.9 Start key: Press this key momentarily to start the test.
2.2.10 Stop key: Press this key momentarily to terminate the test.
2.2.11 Up / Down / Left / Right Button: It is used to select the number of digits when setting the spring.
2.2.12 Numeric keys: Used for spring setting.
2.2.13 Switch / Reverse Switch / Confirmation Key: Used to select and confirm the controls in the interface.
Use and operation
3.1 Measurement interface
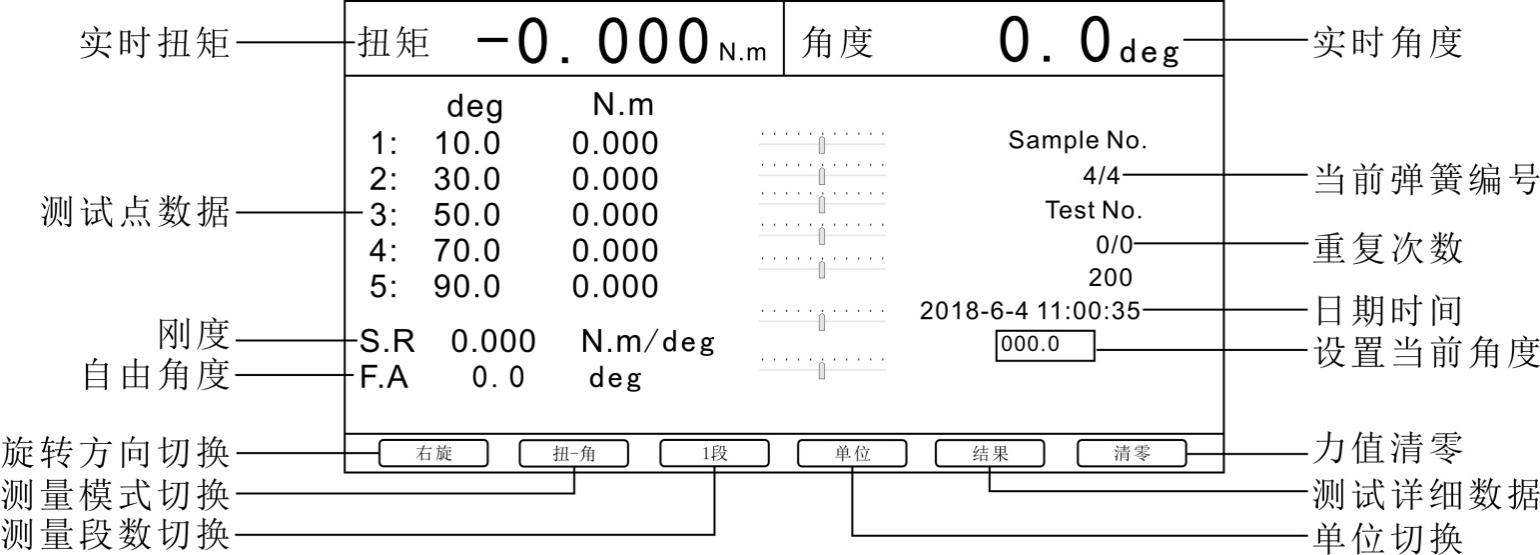
a. The real-time measurement interface mainly displays the real-time torque and angle of the current test; if it is in the test process, records the data of the test point, and also displays the current spring number and the number of repetitions.
b. In the real-time measurement interface, you can switch the spring rotation direction, measurement mode, number of measurement segments and units; the system will save the corresponding settings after the switch.
c. Rotation direction switch: Control the turntable to rotate left or right.
d. Measurement mode switching: It is divided into torsion-angle and angle-torsion. The difference between these two modes is the reference. Torsion-angle records the torque of the spring according to the corresponding angle; angle-torsion records the spring according to the corresponding torque Angle.
e. Number of measurement sections: Test the corresponding spring test points according to the set number of measurement sections. One section is to find the angle or torque of the first test point.
Real-time spring measurement, depending on the type, and angle (relative and absolute) mode selected. The setting value of its operation measurement will also be different.
In the twist-angle mode, select the angle relative mode, then the reference angle of segment 1 to segment 5 needs to be increased, otherwise it will not work properly; if the angle absolute mode is selected, then the reference angle of segment 1 to segment 5 will be required. It is decreasing, otherwise it will not work properly.
3.2 System settings
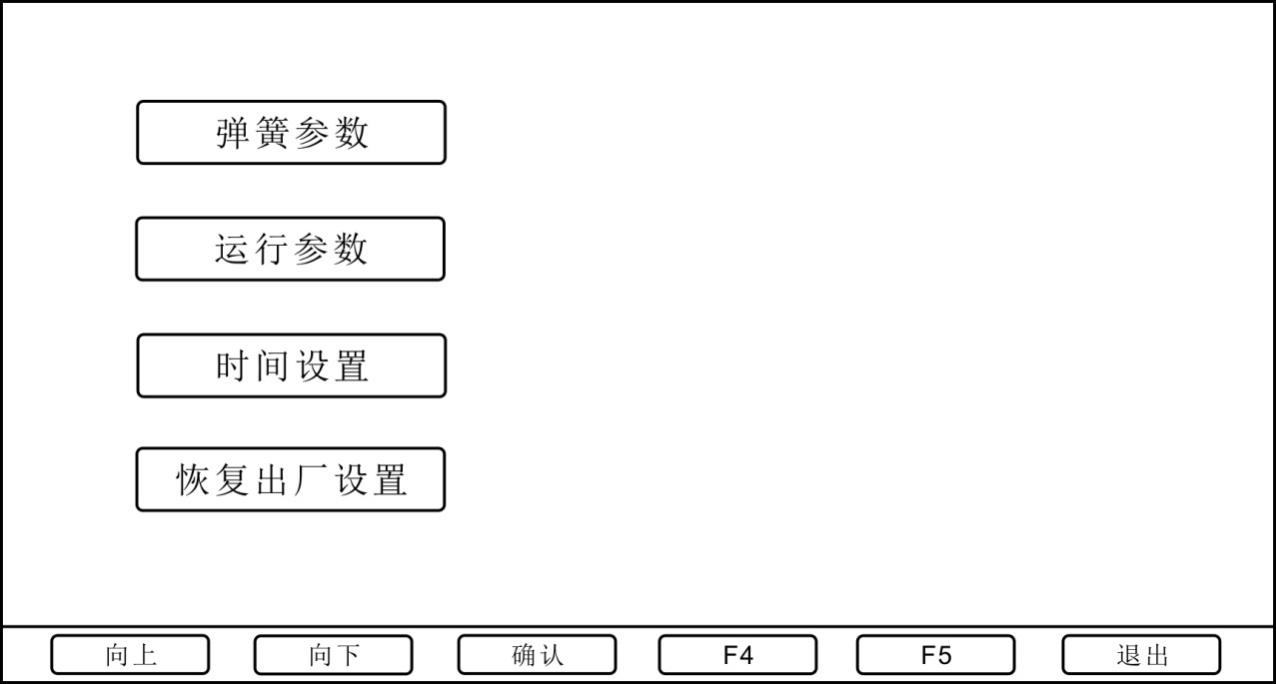
System settings include spring parameter settings, operating parameters, time settings, and factory reset. As shown below:
3.2.1 Spring setting
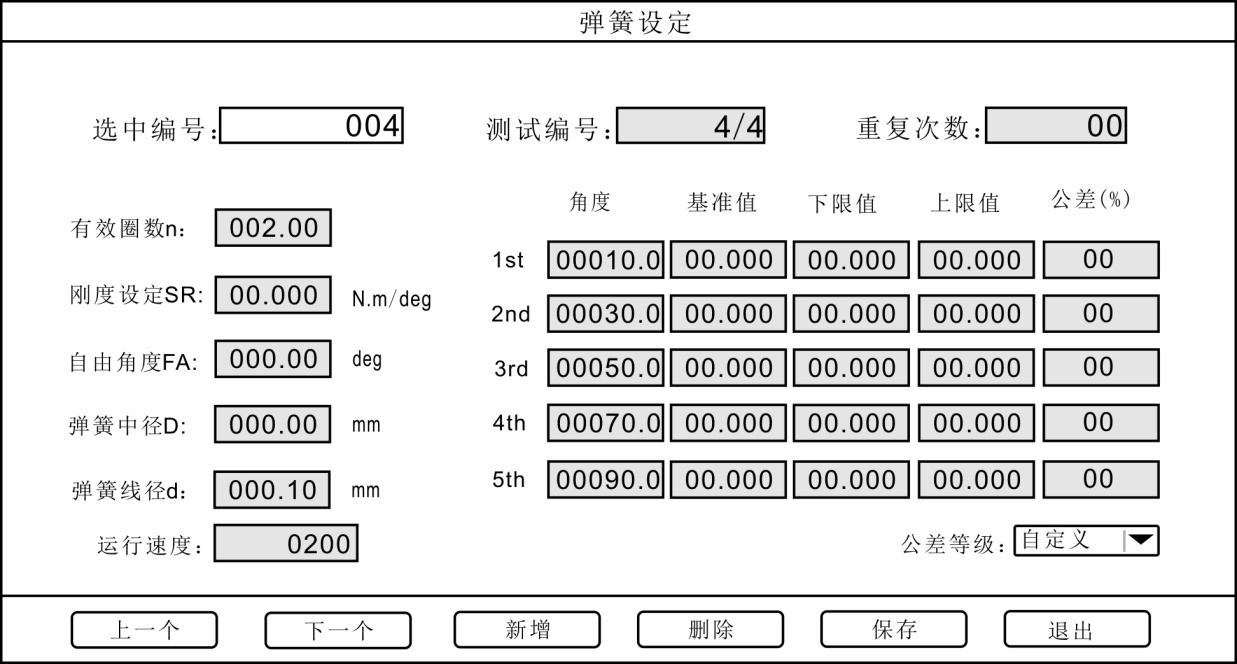
a. Test number: The maximum test number can be set to \"32 \". After pressing \"Add \", the test number is added to one group. Enter the required spring parameters and press \"Save \". As shown below:
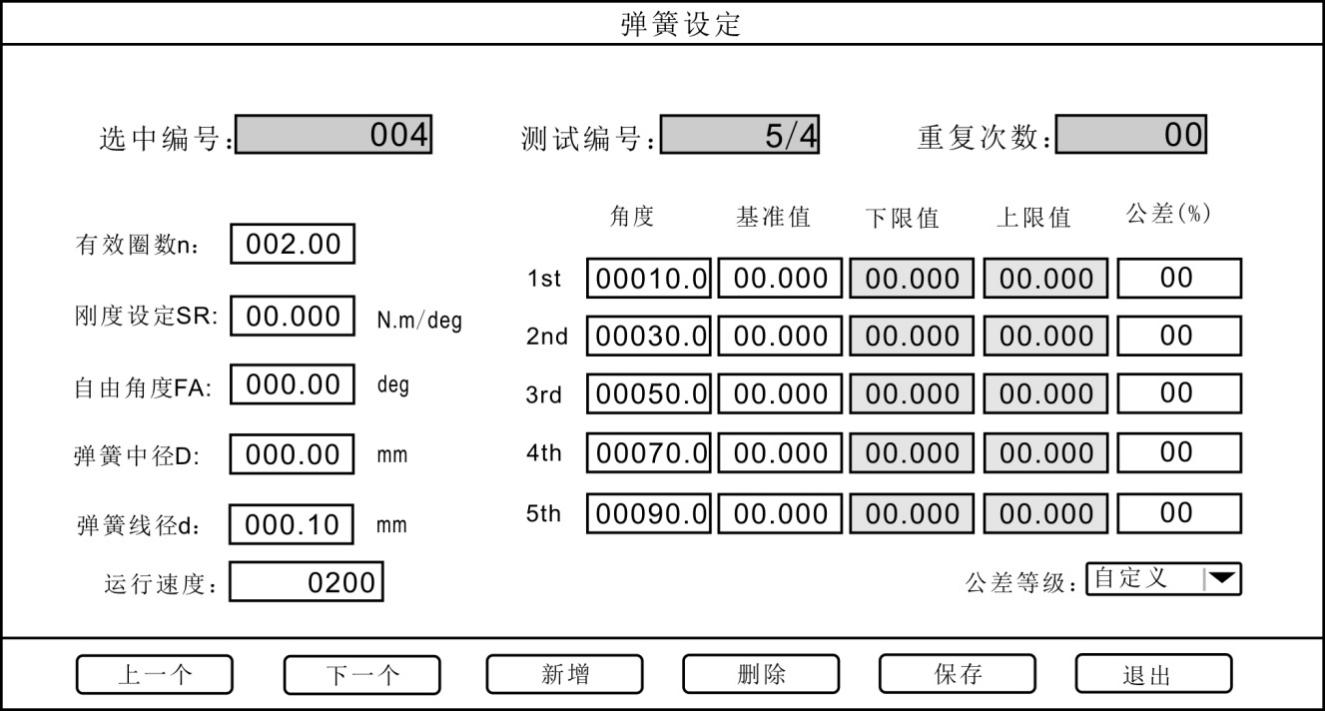
b. Repeat times: The maximum number of repeat times can be set to\"\" 99\". After pressing\" Add\", the test number is increased by one group. Press\"\"SUP\" and\"SDN\" and move the cursor to\"\" Repeat the number of times \", enter the required value, and press\" Save\".
c. Running speed: The running speed during the spring test, expressed as mm / min. The larger the value, the faster the speed.
d. Angle (deg): the position of the spring test point.
e. Reference value: the force value corresponding to the segment point.
f. Tolerance: The setting for determining the qualified range of the spring can be set from \"0% \" to \"99% \". For example, when it is set to\"1% \", the upper limit value is and the lower limit value is. During the spring test, if the force value is within the upper and lower limits, it is qualified.
After setting the spring parameters, press \"Save \". The user can also switch the\"selection number\" to choose different spring settings.
3.2.2 Operating parameters
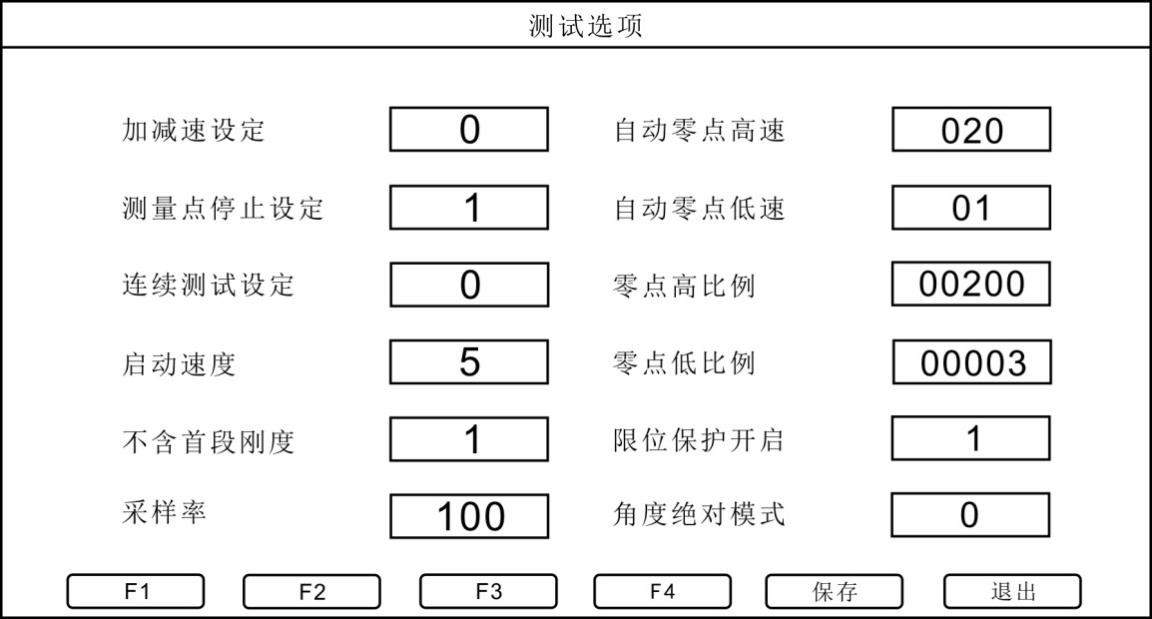
a. Acceleration / deceleration setting: Acceleration / deceleration setting refers to the acceleration setting of the rotary table during measurement. When it is set to\"\" 0\", it is off; when it is set to\"\"1,\" it is on. The acceleration setting and the measurement point stop setting conflict. The acceleration / deceleration setting is effective only when the measurement point stop setting is set to\"\" 0\".
b. Measurement point stop setting: The measurement point stop setting refers to the stop setting of the instrument at each segment point during measurement. When it is set to\"0\", it is turned off; when it is set to\"1\", it is turned on. status. In the open state, if the number of segments is set to\"\" 5 \", the instrument will stop once at these 5 segment points when measuring; if in the off state, the instrument will not stop at the segment points during measurement.
c. Continuous test setting: Repeat test setting, when set to\"0\", it is off; when set to\"1\", it is on.
d. Startup speed: The startup speed setting is only valid when the acceleration / deceleration setting is turned on. The startup speed can be set to \"1 \" to \"5 \". When set to\"1\", that is, the acceleration during measurement is from 1mm / min to 100mm / min, the larger the value is set, the faster the acceleration starts. The speed setting unit is mm / min. The startup speed cannot be set to\"0\".
e. The stiffness of the first segment is not included: When the stiffness of the first segment is not set to\"\" 1 \", it is turned on. For example, if 5 segments are set, the instrument will not calculate the stiffness of the first segment when calculating the average stiffness. If \"0 \", it is closed.
f. Sampling rate: The number of samples per second of the instrument, which can be set from \"1 \" to \"100 \".
g. Automatic zero-point high-speed: high-speed setting of automatic origin, the unit is \"mm / min \". After pressing the auto origin button during measurement, the spring will return to a position relatively close to the origin at the set auto zero high-speed value.
h. Automatic zero low speed: Automatic zero low speed is a value set on the basis of automatic zero high speed. The unit is \"mm / min \". When the spring returns to a position relatively close to the origin, the automatic zero-point low-speed start will make the spring return to the origin more accurately.
i. Zero high ratio / zero low ratio: These two parameters are the force value determination of the automatic origin. The zero height ratio is \"200 \", that is, this force value is full scale * 200/10000, which is 2% of full scale. The zero low ratio is \"3 \", that is, this force value is full scale * 3/10000, which is 0.03% of full scale. After starting the automatic origin, when the force value is close to 2% of the full scale, the instrument will stop at the position of the automatic origin according to the low-scale force value after a few seconds of pause of this force value.
j. Angle absolute mode: When set to \"1 \", it is angle absolute mode; when it is set to \"0 \", it is displacement relative mode. For relative measurement mode and absolute measurement mode, the difference is the set angle. The relative measurement mode is how many angles are rotated, while the absolute measurement mode is expressed as how many angles are rotated.
Relative measurement mode, the angle required to set the number of spring segments, ANGLE1 < ANGLE2 < ... < ANGLE5
At the same time, the torque setting is also required, TORQUE1 < TORQUE2 < ... < TORQUE5
The absolute measurement mode will have different setting parameters for different spring types.
ANGLE1 > ANGLE2 > ... > ANGLE5
3.2.3 Time setting
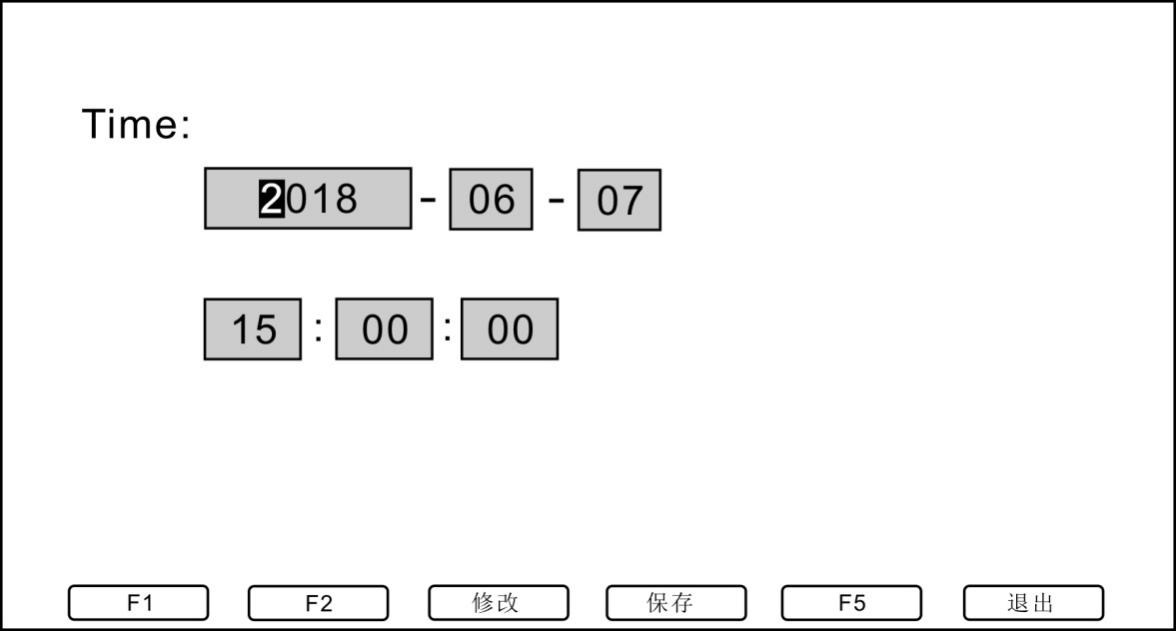
Time setting is used to set the time displayed on the measurement interface and the printing time.
3.2.4 Restore factory settings
Press this key to restore the instrument to factory settings and restart automatically.
3.3 Operation steps
3.3.1 Make sure the power cord is connected.
3.3.2 Turn on the power switch.
3.3.3 Select the rotation direction, unit, measurement mode and number of measurement segments.
3.3.4 Enter spring parameter setting and running parameter setting.
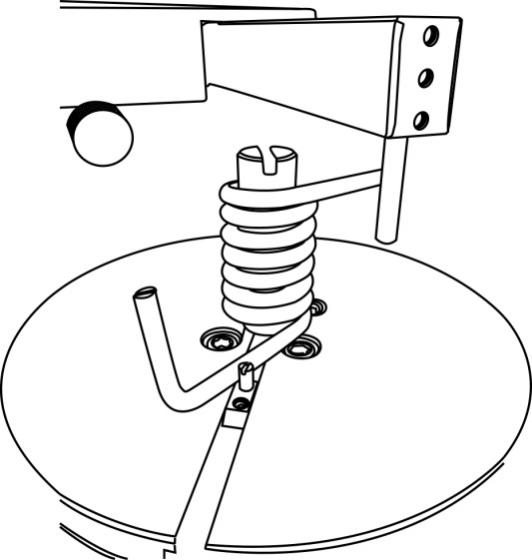
3.3.5 Place the spring on the rotary table, as shown in the figure below:
3.3.6 In the measurement interface, press \"START \" to start the test, and press \"PRINT \" to print the measurement data after completion.
3.4 Data export
3.4.1 Using the communication interface, real-time measurement data can be exported through the communication protocol provided by the Division.
Fourth, daily maintenance and maintenance
4.1 The environment shall be kept clean to prevent liquids, iron filings and other substances from entering the instrument and damaging the electronic components.
4.2 Please clean the instrument with a soft cloth, immerse the cloth in water soaked with detergent, wring it dry, and then remove dust and dirt.
Note: Do not use volatile chemicals to clean the instrument (such as volatile agents, thinners, alcohol, etc.).
4.3 Do not operate this machine in the following environments
a, humid environment
b. Dusty environment
c. Where oil or chemicals are used
d. Places with earthquake sources around
4.4 When not in use for a long time, unplug the power plug, and do dustproof and moistureproof treatment.
Five, random attachments